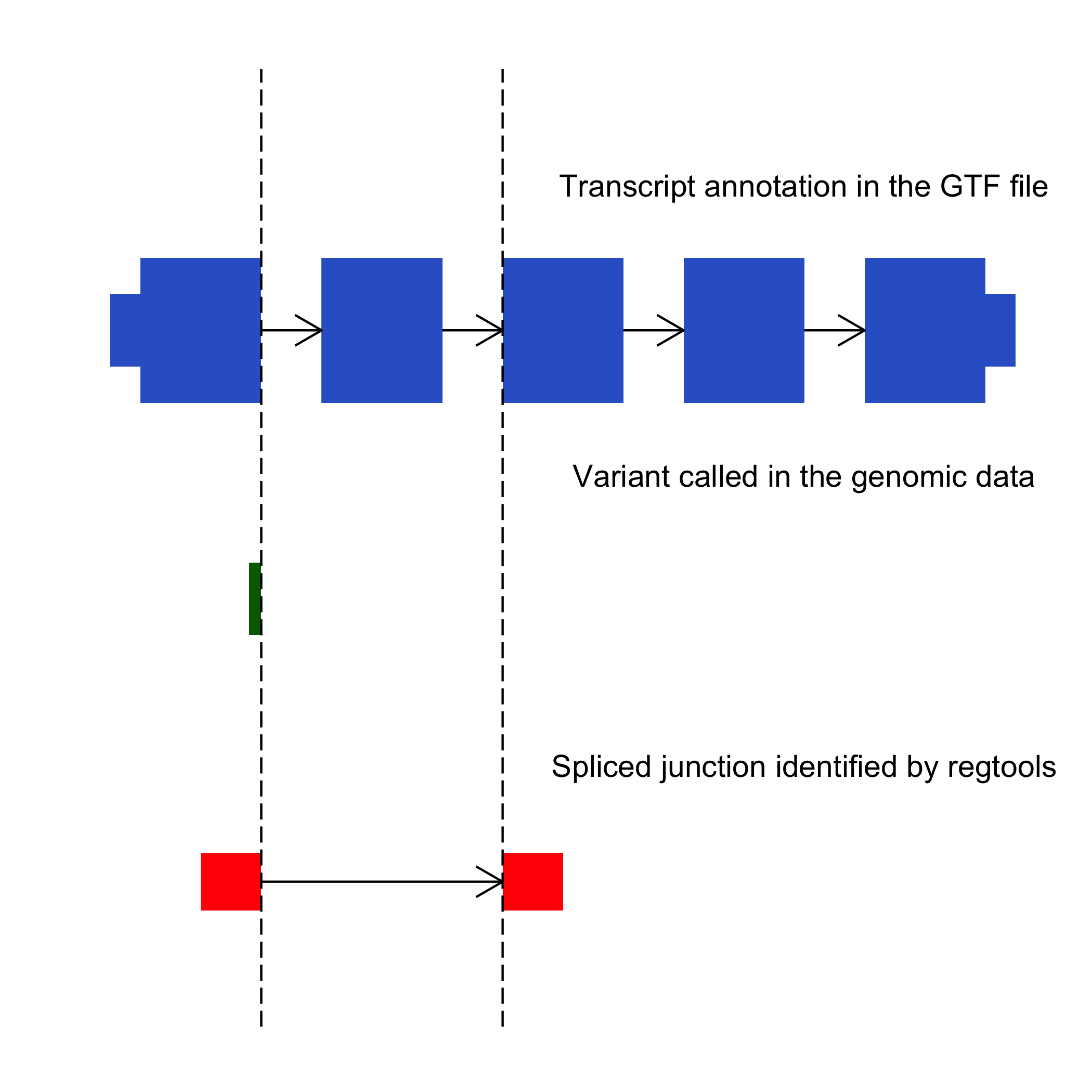
Overview of cis-splice-effects associate command
The cis-splice-effects associate command is used to identify splicing misregulation events. This command is similar to cis-splice-effects identify, but takes the BED output of junctions extract in lieu of a BAM file with RNA alignments. The tool then proceeds to associate non-canonical splicing junctions near the variant sites.
Usage
regtools cis-splice-effects associate [options] variants.vcf junctions.bed ref.fa annotations.gtf
Input
| Input | Description |
|---|---|
| variants.vcf | Variant call in VCF format from which to look for cis-splice-effects. |
| junctions.bed | BED file of junctions to look through for evidence of splice events. The file is expected to be in the BED12 format of the junctions extract output. |
| ref.fa | The reference FASTA file. The donor and acceptor sequences used in the "splice-site" column of the annotated junctions are extracted from the FASTA file. |
| annotations.gtf | The GTF file specifies the transcriptome that is used to annotate the junctions and variants. For examples, the Ensembl GTFs for release78 are here. |
Note - Please make sure that the version of the annotation GTF that you use corresponds with the version of the assembly build (ref.fa) and that the co-ordinates in the VCF file are also from the same build.
Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -o STR | Output file containing the aberrant splice junctions with annotations. [STDOUT] |
| -v STR | Output file containing variants annotated as splice relevant (VCF format). |
| -j STR | Output file containing the aberrant junctions in BED12 format. |
| -w INT | Window size in b.p to associate splicing events in. The tool identifies events in variant.start +/- w basepairs. Default behaviour is to look at the window between previous and next exons. |
| -e INT | Maximum distance from the start/end of an exon to annotate a variant as relevant to splicing, the variant is in exonic space, i.e a coding variant. [3] |
| -i INT | Maximum distance from the start/end of an exon to annotate a variant as relevant to splicing, the variant is in intronic space. [2] |
| -I | Annotate variants in intronic space within a transcript(not to be used with -i). |
| -E | Annotate variants in exonic space within a transcript(not to be used with -e). |
| -S | Don't skip single exon transcripts. |
Output
For an explanation of the annotated junctions that are identified by this command please refer to the output of the junctions annotate command here
For an explanation of the annotated variants that are identified by this command when using the -v option, please refer to the output of the variants annotate command here
Examples